数据结构作业三:双向链表与静态链表_双向静态链表 删除-程序员宅基地
双向链表:
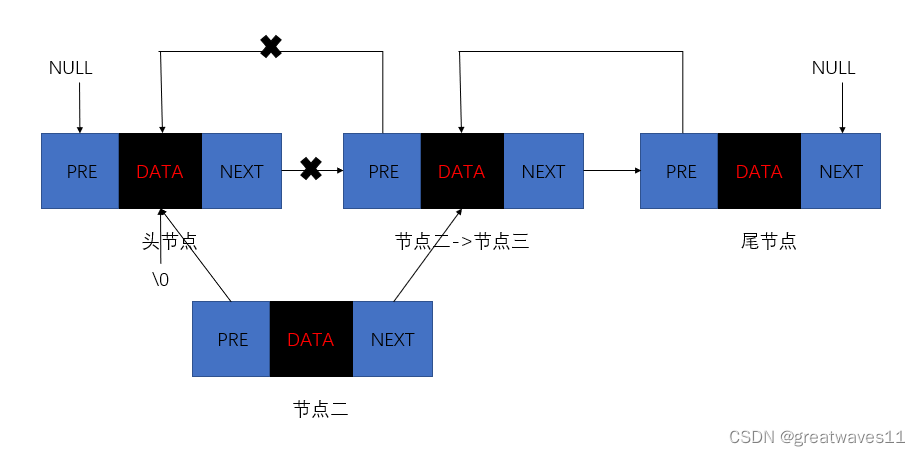
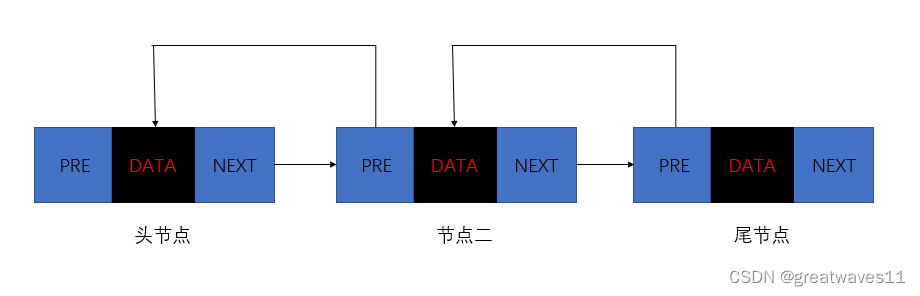
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据 结点 中都有两个 指针 ,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。 所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。
一,结构体定义及宏
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/**
* 定义字符双向链表。
*/
typedef struct DoubleLinkNode{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkNode *previous;
struct DoubleLinkNode *next;
} DLNode, *DLNodePtr;二,初始化双向链表
/**
* 初始化头节点。
* @return 返回头节点的指针。
*/
DLNodePtr initLinkList(){
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}三,打印双向链表
/**
* 打印链表。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
*/
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader){
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
if(p == NULL){
printf("The list is empty.");
}
while(p != NULL){
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}四,在给定的位置插入元素
/**
* 在给定的位置加入元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
* @param paraPosition 给定的位置。
*/
void insertElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
// Step 1. 搜索给定的位置。
p = paraHeader;
for(int i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++){
p = p->next;
if(p == NULL){
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
// Step 2. 创建一个新节点
q = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkNode));
q->data = paraChar;
// Step 3. 链接链表和节点。
printf("linking\r\n");
r = p->next;
q->next = p->next;
q->previous = p;
p->next = q;
if (r != NULL){
r->previous = q;
}
}五,删除指定元素
/**
* 删除链表中的元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
*/
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
// Step 1. 定位
while((p->next != NULL) && (p->next->data != paraChar)){
p = p->next;
}
// Step 2. 检查错误
if(p->next == NULL){
printf("The char %c does not exist.\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
// Step 3. 改变链接
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if(r != NULL){
r->previous = p;
}
// Step 4. 释放内存
free(q);
} 六,找到双向链表中特定数据的位置
六,找到双向链表中特定数据的位置
/**
* 找到双向链表中特定的数据的位置
*/
void locateElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p;
p = paraHeader;
while(p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
if(p->data == paraChar){
printf("Found the char %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
}
printf("The char %c is not been found.\r\n", paraChar);
return ;
}七,删除双向链表
void LinkDestory(DLNodePtr paraHeader){
DLNodePtr p;
p = paraHeader;
p->next = NULL;
printf("The list has been destoryed.\r\n");
return;
}八,函数功能测试
/**
* 功能测试。
*/
void insertDeleteTest(){
// Step 1. 初始化一个空链表。
DLNodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
// Step 2. 加入一些字符。
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 5);
printList(tempList);
// Step 3. 删除一些字符(第一次出现的)。
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
// Step 4. 在链表给定位置插入特定元素。
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 1);//首位插入
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 5);//末位插入
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 3);//中间插入
printList(tempList);
// Step 5. 查找指定元素
locateElement(tempList, 'H');
locateElement(tempList, 'l');
locateElement(tempList, 'o');
locateElement(tempList, 'a');
// Step 6. 清空链表
LinkDestory(tempList);
printList(tempList);
}在老师的基础上,加入了对插入功能的更进一步的测试,同时加入了更多的打印函数来更好地了解函数地运行规律,之后又加入了对locateElement函数地测试。
九,对于链表地址地测试
/**
* 地址测试.
*/
void basicAddressTest(){
DLNode tempNode1, tempNode2;
tempNode1.data = 4;
tempNode1.next = NULL;
tempNode2.data = 6;
tempNode2.next = NULL;
printf("The first node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode1, &tempNode1.data, &tempNode1.next);
printf("The second node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode2, &tempNode2.data, &tempNode2.next);
tempNode1.next = &tempNode2;
}十,程序入口
/**
* 程序入口。
*/
int main(){
insertDeleteTest();
basicAddressTest();
}十一,运行结果
The list is empty.
linking
H
linking
He
linking
Hel
linking
Hell
linking
Hello
linking
Hello!
Hllo!
The char a does not exist.
Hllo!
Hll!
linking
Holl!
linking
Holl!o
linking
Holol!o
Found the char H
Found the char l
Found the char o
The char a is not been found.
The list has been destoryed.
The list is empty.
The first node: 6421968, 6421968, 6421984
The second node: 6421936, 6421936, 6421952静态链表
静态链表,也是线性存储结构的一种,它兼顾了顺序表和链表的优点于一身,可以看做是顺序表和链表的升级版。
使用静态链表存储数据,数据全部存储在数组中(和顺序表一样),但存储位置是随机的,数据之间"一对一"的逻辑关系通过一个整形变量(称为"游标",和指针功能类似)维持(和链表类似)。
例如,使用静态链表存储 {1,2,3} 的过程如下:
创建一个足够大的数组,假设大小为 6,如图一所示:

图 一 空数组
接着,在将数据存放到数组中时,给各个数据元素配备一个整形变量,此变量用于指明各个元素的直接后继元素所在数组中的位置下标,如图 2 所示:
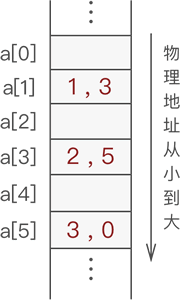
图 二 静态链表存储数据
通常,静态链表会将第一个数据元素放到数组下标为 1 的位置(a[1])中。
图 2 中,从 a[1] 存储的数据元素 1 开始,通过存储的游标变量 3,就可以在 a[3] 中找到元素 1 的直接后继元素 2;同样,通过元素 a[3] 存储的游标变量 5,可以在 a[5] 中找到元素 2 的直接后继元素 3,这样的循环过程直到某元素的游标变量为 0 截止(因为 a[0] 默认不存储数据元素)。
类似图 2 这样,通过 "数组+游标" 的方式存储具有线性关系数据的存储结构就是静态链表。
一,结构体定义及宏
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 5
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
} *ListPtr;二,初始化静态链表
/**
* 初始化头节点。
* @return 返回头节点的指针。
*/
ListPtr initLinkedList(){
// 指向整个链表空间的指针
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
// 分配总空间
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
// 第一个节点是头结点
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
// 初始化时只有头结点使用
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}
return tempPtr;
}三,打印静态链表
/**
* 打印链表。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
*/
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr){
int p = 0;
while (p != -1) {
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}四,在给定的位置插入元素
/**
* 在给定的位置加入元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
* @param paraPosition 给定的位置。
*/
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
int p, q, i;
// Step 1. 搜索位置
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
// Step 2. 创建一个新的节点
for ( i; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0){
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}
}
if (i >= DEFAULT_SIZE){
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
// Step 3. 链接节点
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}五,删除指定元素
/**
* 删除链表中的元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
*/
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar){
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar)){
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1) {
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
// 此语句和free(q)功能相同
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}六,函数功能测试
/**
* 功能测试。
*/
void appendInsertDeleteTest(){
// Step 1. 初始化一个空链表
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
// Step 2. 加入一些元素
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
// Step 3. 删除一些元素(首次出现的该元素)
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
printList(tempList);
}增加了部分的打印函数以更好地理解函数功能。
七,程序入口
/**
* 程序入口
*/
void main(){
appendInsertDeleteTest();
}八,运行结果
Space at 1 allocated.
linking
Space at 2 allocated.
linking
Space at 3 allocated.
linking
Space at 4 allocated.
linking
No space.
No space.
Hlel
Deleting 'e'.
Deleting 'a'.
Cannot delete a
Deleting 'o'.
Cannot delete o
Hll
Space at 2 allocated.
linking
Hxll完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/**
* 定义字符双向链表。
*/
typedef struct DoubleLinkNode{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkNode *previous;
struct DoubleLinkNode *next;
} DLNode, *DLNodePtr;
/**
* 初始化头节点。
* @return 返回头节点的指针。
*/
DLNodePtr initLinkList(){
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}
/**
* 打印链表。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
*/
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader){
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
if(p == NULL){
printf("The list is empty.");
}
while(p != NULL){
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
/**
* 在给定的位置加入元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
* @param paraPosition 给定的位置。
*/
void insertElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
// Step 1. 搜索给定的位置。
p = paraHeader;
for(int i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++){
p = p->next;
if(p == NULL){
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
// Step 2. 创建一个新节点
q = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkNode));
q->data = paraChar;
// Step 3. 链接链表和节点。
printf("linking\r\n");
r = p->next;
q->next = p->next;
q->previous = p;
p->next = q;
if (r != NULL){
r->previous = q;
}
}
/**
* 删除链表中的元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
*/
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
// Step 1. 定位
while((p->next != NULL) && (p->next->data != paraChar)){
p = p->next;
}
// Step 2. 检查错误
if(p->next == NULL){
printf("The char %c does not exist.\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
// Step 3. 改变链接
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if(r != NULL){
r->previous = p;
}
// Step 4. 释放内存
free(q);
}
/**
* 找到双向链表中特定的数据的位置
*/
void locateElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p;
p = paraHeader;
while(p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
if(p->data == paraChar){
printf("Found the char %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
}
printf("The char %c is not been found.\r\n", paraChar);
return ;
}
void LinkDestory(DLNodePtr paraHeader){
DLNodePtr p;
p = paraHeader;
p->next = NULL;
printf("The list has been destoryed.\r\n");
return;
}
/**
* 功能测试。
*/
void insertDeleteTest(){
// Step 1. 初始化一个空链表。
DLNodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
// Step 2. 加入一些字符。
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 5);
printList(tempList);
// Step 3. 删除一些字符(第一次出现的)。
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
// Step 4. 在链表给定位置插入特定元素。
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 1);//首位插入
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 5);//末位插入
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 3);//中间插入
printList(tempList);
// Step 5. 查找指定元素
locateElement(tempList, 'H');
locateElement(tempList, 'l');
locateElement(tempList, 'o');
locateElement(tempList, 'a');
// Step 6. 清空链表
LinkDestory(tempList);
printList(tempList);
}
/**
* 地址测试.
*/
void basicAddressTest(){
DLNode tempNode1, tempNode2;
tempNode1.data = 4;
tempNode1.next = NULL;
tempNode2.data = 6;
tempNode2.next = NULL;
printf("The first node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode1, &tempNode1.data, &tempNode1.next);
printf("The second node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode2, &tempNode2.data, &tempNode2.next);
tempNode1.next = &tempNode2;
}
/**
* 程序入口。
*/
int main(){
insertDeleteTest();
basicAddressTest();
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 5
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
} *ListPtr;
/**
* 初始化头节点。
* @return 返回头节点的指针。
*/
ListPtr initLinkedList(){
// 指向整个链表空间的指针
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
// 分配总空间
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
// 第一个节点是头结点
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
// 初始化时只有头结点使用
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}
return tempPtr;
}
/**
* 打印链表。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
*/
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr){
int p = 0;
while (p != -1) {
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
/**
* 在给定的位置加入元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
* @param paraPosition 给定的位置。
*/
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
int p, q, i;
// Step 1. 搜索位置
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
// Step 2. 创建一个新的节点
for ( i; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0){
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}
}
if (i >= DEFAULT_SIZE){
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
// Step 3. 链接节点
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}
/**
* 删除链表中的元素。
* @param paraHeader 是链表的头结点。
* @param paraChar 给定的char元素。
*/
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar){
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar)){
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1) {
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
// 此语句和free(q)功能相同
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}
/**
* 功能测试。
*/
void appendInsertDeleteTest(){
// Step 1. 初始化一个空链表
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
// Step 2. 加入一些元素
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
// Step 3. 删除一些元素(首次出现的该元素)
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
printList(tempList);
}
/**
* 程序入口
*/
void main(){
appendInsertDeleteTest();
}智能推荐
桌面开发者的界面故事,该醒醒了-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读43次。本文我们只谈界面。 大部分人最开始学习编程是Console,搞个计算器啥的,后来高级一点能做一个俄罗斯方块出来。很羡慕那些能做出界面的,于是大二学了MFC,一开始看《深入浅出》怎么都搞不懂,后来我们班的一个女生教了我两个小时,我一下子通畅了,用GDI半个月苦哈哈的做了第一个当时觉得还能看得界面(不用任何控件哦)连箭头都是用三根线拼起来的! ...
解决C语言创建链表时出现的问题:引发了异常: 读取访问权限冲突_c语言链表创建时出现访问权限冲突怎么办-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读715次,点赞11次,收藏12次。这里可以看到,在打印时传入的地址与1中的head地址并不相同,从而在读取链表head地址时并不是1中的head的地址,也就出现了如上的情况。这里楼主也不清楚具体是什么导致了传入地址的变化,还望有大佬指点。我也参考了另一位楼主的解决办法,如下。既然通过逐行运行得知是传入PrintList的地址不一致而导致的,那么这里将CreateList函数的类型进行修改,并返回head的地址。当数据元素输入完后,红圈这里head指向的地址我们先记住,接下来我们对输入的数据进行打印。第一次写文章,如有问题还望有大佬指点。_c语言链表创建时出现访问权限冲突怎么办
Added a key not lexically larger than previous.-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.2k次。跑批问题:Caused by: java.io.IOException: Added a key not lexically larger than previous. Current cell = 10000000414/aml_custinfo:address/1594509705240/Put/vlen=42/seqid=0, lastCell = 10000000414/aml_custinfo:watchcustflag/1594509705240/Put/vlen=1/seqid=0报错_added a key not lexically larger than previous
查看linux服务器 频率,LInux查看服务器硬件信息-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读378次。Hi,大家好;今天是双12,大家剁手了没。今天给大家带来的是《Linux查看服务器上的硬件信息》本篇文章的示例全部是在服务器(Inspur SA5112M4)上实现的,有些命令在虚拟机上达不到效果查看服务器型号、序列号root@zhangdaifu# dmidecode -s system-serial-numberroot@zhangdaifu# dmidecode -t system | gr..._crystal beach /dma
MATLAB一元函数与二元函数求极小值_matlab中求解2变量函数的极小值-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次,点赞3次,收藏6次。MATLAB一元函数与二元函数求极小值_matlab中求解2变量函数的极小值
MySQL学习_mysql possible key有值但是key为null-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读734次。Mysql的三大范式,存储引擎、索引、sql的执行计划、count()计数的区别,事务,简单sql调优,索引失效场景、jdbcTemplate查询类获取时间没有时分秒、连接mysql时区配置,jaskson转json时区配置..._mysql possible key有值但是key为null
随便推点
【数据结构】八大排序之快速排序算法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次,点赞25次,收藏29次。数据结构快速排序详解.内容包括:快排的简介及思想,快排代码实现的三种方式,快排的时间复杂度分析,快排的优化,快排的非递归实现,快排的三路划分算法.
PHP判断是否手机端或PC端访问_php判断手否电脑端-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读461次。1.在PublicController控制器中写好判断手机端方法。<?phpnamespace Home\Controller;use Think\Controller;class PublicController extends Controller { //判断是否是手机端还是电脑端 function isMobile(){ // 如果有Ht_php判断手否电脑端</div>
python将列表元素连接_python中列表元素连接方法join用法实例-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.9k次。本文实例讲述了python中列表元素连接方法join用法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下:创建列表:>>> music = ["Abba","Rolling Stones","Black Sabbath","Metallica"]>>> print music输出:['Abba', 'Rolling Stones', 'Black Sabbath', 'Me..._python将list使用/n连接起来
HTML表格标签的基础用法与实例_html表格例子-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读561次。文章目录一、表格的作用二、表格骨架标签三、表格的样式四、表格其他标签五、合并单元格六、综合练习一、表格的作用在CSS还未普及的时候一些简单的网站使用表格布局是十分快捷的,开发人员只要按照需求,简单的对表格进行行列的拆分,就能实现设计页面的布局;随着互联网的发展以及CSS的普及用户的审美提升,表格布局渐渐淡出了布局手段行列。虽然表格现在不常用于布局,但是在展示一些后台数据的时候表格可以让数据显示的非常清晰规整,阅读起来十分方便,所以我们常用表格来展示一些数据。二、表格骨架标签<table>_html表格例子
[C方向]作业集锦_方向作业-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读284次。## 点击蓝色字体可跳转至相应文章,尔后文章待续... 1.New Code day11. 打印100~200 之间的素数 2. 输出乘法口诀表 3. 判断1000年---2000年之间的闰年 2.New Code day21.给定两个整形变量的值,将两个值的内容进行交换。 2.不允许创建临时变量,交换两个数的内容(附加题) 3.求10 个整数中最大值。 ..._方向作业
Kubernetes高可用集群二进制部署(四)部署kubectl和kube-controller-manager、kube-scheduler_kube-controller-manager 配置-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1k次,点赞11次,收藏8次。scheduler通过 kubernetes 的监测(Watch)机制来发现集群中新创建且尚未被调度到 Node 上的 Pod。 scheduler会将发现的每一个未调度的 Pod 调度到一个合适的 Node 上来运行。 scheduler会依据下文的调度原则来做出调度选择。Controller Manager作为集群内部的管理控制中心,负责集群内的Node、Pod副本、服务端点(Endpoint)、命名空间(Namespace)、服务账号(ServiceAccount)、资源定额(ResourceQuot_kube-controller-manager 配置